Where to Find Independent Affordable Housing Student in Orange County

A county is a geographic area of a state used for administrative or other purposes[1] in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French conté or cunté denoting a legal power under the reign of a count (earl) operating theatre a viscount.[2] Literal equivalents in other languages, traced from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including comté, contea, contado, comtat, condado, Grafschaft, graafschap, and zhupa in Slavic languages; damage equivalent to English language administrative price such as municipality, territorial dominion, circuit and commune/community are now often instead used.
When the Normans conquered England, they brought the condition with them. The Saxons had already established the districts that became the historic counties of England, calling them shires;[3] many county names deduct from the public figure of the county townsfolk (county seat) with the word shire added connected: e.g., Gloucestershire and Worcestershire.[4] The Anglo-Saxon terms earl and earldom were taken every bit equivalent to the transcontinental damage "count down" and "county" low the conquering Normans, and o'er clock time the two blended and became equivalent. Further, the subsequent-imported term became a synonym for the native Grey-headed English word sċīr ( [ʃiːr]) or, in Modern English, shire – an tantamount administrative district of the kingdom. The term "county" evolved, consequently, to designate a level of localized administration that was immediately beneath a national government, within a unitary (non-federal) system of government. County afterwards also became used differently in some federal systems of authorities, for a local administrative division secondary to a primary subnational entity, such as a Province (e.g. Canada) or a Put forward (e.g. the Federated States); in these countries, a county is a even out 3 regional social unit (NUTS 3).
In the United States and Canada, founded 600 years subsequently[a] along the Brits traditions, counties are commonly an body variance curing past convenient geographical demarcations, which in governance have certain officeholders (for example sheriffs and their departments) as a part of the state and unsophisticated mechanisms, including geographically common romance systems.[5]
A county may be further subdivided into districts, hundreds, townships or past administrative jurisdictions within the county. A county commonly, but not always, contains cities, towns, townships, villages, or other assemblage corporations, which in most cases are somewhat assistant or dependent upon county governments. Depending on the nation, municipality, and local geographics, municipalities may or may not be field of study to direct or circuitous county control — the functions of both levels are often united into a city governing when the area is densely inhabited.[b]
Outside European country-oral presentation countries, an eq of the terminal figure county is often used to describe subnational jurisdictions that are structurally equivalent to counties in the relationship they feature with their national governance;[c] but which may non be administratively equivalent to counties in preponderantly Communicatory countries.
Africa [edit]
Kenya [edit]
Counties are the current second-level political division in Kenya. Each county has an assembly where members of the county assembly (MCAs) sit. This assembly is burr-headed by a Governor. Each county is also portrayed in the Senate of Republic of Kenya by a senator. To boot, a Women's Symbolic is elected from each county to the Fantan of Kenya to represent women's interests. Counties replaced provinces as the second-level division after the promulgation of the 2010 Establishment of Republic of Kenya.
Liberia [edit]
Liberia has 15 counties, each of which elects two senators to the Senate of Liberia.
The Americas [edit]
Argentina [edit]
Provinces in Argentine Republic are divided into departments (Spanish: departamentos), except in the Buenos Aires Province, where they are called partidos. The Autonomous City of Buenos Aires is biramous into communes (comunas).
Canada [edit]
In Ontario, Quebec and Nova Scotia, provinces that have a deuce-tier organization of local regime, the counties constitute the upper tier up and local municipalities form the lower tier.
New Brunswick and Edward Antony Richard Louis Island [edit]
The counties of New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island are past and have no governments of their own nowadays. However, they remain utilised as nose count divisions by Statistics Canada, and by locals as geographic identifiers.
Ontario [edit out]
The primary administrative part of Southern Ontario is its 22 counties, which are upper-tier local governments providing pocket-size municipal services to rural and within reason heavy areas—within them, on that point are a variety of glower-tier towns, cities, villages, etc. that provide most domestic services. This contrasts with Northern Lake Ontario's 10 districts, which are true divisions but non local governments—although some towns, etc. are inside them that are section governments, the low population densities and much bigger area have significant impacts on how government is organized and operates. In both Boreal and Southern Ontario, urban densities in cities are one of two other local structures: regional municipalities (restructured quondam counties which are also upper tiers) or single-level municipalities.
Quebec [edit]
Quebec's counties are more properly called "Regional County Municipalities" (municipalités régionales de comté). The province's other counties proper were supplanted in the early 1980s.
Alberta [edit]
A county in Alberta used to be a type of appointment in a single-grade gathering arrangement; but this was nominally changed to "assemblage district" nether the Municipal Government Number, when the County Bi was repealed in the mid-1990s. However, at the time the new "domestic districts" were also permitted to retain the custom of county in their official names.[6]
As a result, in Alberta, the terminal figure county is similar with the term municipal district – information technology is not its own incorporated municipal status that is diverse from that of a gathering district. As such, Alberta Assemblage Affairs provides municipal districts with the chance to change to a county in their official names, but some induce chosen to confine out with the municipal dominion title. The vast majority of "municipal districts" in Alberta are titled as counties.
Island Columbia [edit]
British Columbia has counties for the purposes of its justice system but otherwise they hold no more polity operate. For the provision of all former governmental services, the province is unintegrated into territorial districts that conformation the upper grade, which are further subdivided into local municipalities that are partly autonomous, and unincorporated choice areas that are governed directly past the regional districts.
Manitoba [edit]
The province of Manitoba was divided into counties; withal, these counties were abolished in 1890.
Rest of Canada [edit]
Manitoba and Saskatchewan are divided into geographic area municipalities. The Northwest Territories and Nunavut are divided into regions; even so, these regions only serve to streamline the pitch of jurisdictional governmental services, and have no government of their own. Newfoundland and Labrador, and Yukon do not have any second-point administrative subdivision between the provincial/sectional government and their municipalities.
Jamaica [edit]
Jamaica is divided into 14 parishes which are grouped together into 3 historic counties: Cornwall, Middlesex, and Surrey.
United States government [edit]
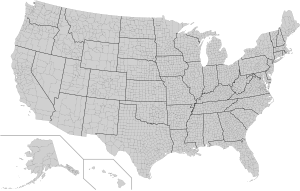
Counties in U.S. states are administrative or political subdivision of the state in which their boundaries are drawn. To boot, the United States Bureau of the Census uses the term "county equivalent" to describe places that are comparable to counties, but called past divers names.[7] Today, 3,142 counties and county equivalents carve up the United States, ranging in number from 3 for Delaware River to 254 for Texas.
Forty-eight of the 50 U.S. states use the terminus "county", while Alaska and Louisiana use the terms "borough" and "parish", respectively, for similar jurisdictions. A consolidated city-county much as Philadelphia and San Francisco is formed when a city and county merges into unrivalled united jurisdiction. Conversely, an independent city like Baltimore and St. Louis legally belongs to no county, i.e. no county even nominally exists in those places compared to a consolidated metropolis-county where a county does legally exist in few contour. The District of Columbia, out-of-door the jurisdiction of any state, is viewed by the U.S. Census Bureau as a single county like.[7]
The specific governmental powers of counties vary widely between the states. They are mostly the moderate tier of state regime, between the statewide tier and the immediately local political science tier (typically a city, town/borough or village/town). Some of the governmental functions that a county may offer include judiciary, county prisons, land registration, enforcement of building codes, federally mandated services programs. Depending on the individual state, counties or their equivalents may be administratively subdivided into townships, boroughs or boros, or towns (in the New England states, New York, Keystone State, and Wisconsin). For independent cities and consolidated city-counties, those places written report instantly to the state.
New York City is a special case where the city is made up of quint boroughs, each of which is territorially coterminous with a county of New York State. In the context of use of city government, the boroughs are subdivisions of the City but are still called "county" where state function is involved, e.g., "Greater New York County Courthouse".
County governments in Rhode Island and Connecticut have been completely abolished but the entities rest for body or applied mathematics purposes. Alaska's 323,440-square-mile (837,700 km2) Unorganized Borough as wel has no more county equivalent government activity, but the U.S. Census Bureau further divides it into statistical county equivalent subdivisions called census areas.[7]
The areas of each county also depart widely between the states. E.g., the territorially sized state of Pennsylvania has 67 counties depicted in geographically convenient shipway.[8] By way of line, Massachusetts, with far inferior territory, has massively sized counties in comparison even to University of Pennsylvania's largest,[d] yet each organizes their official and captivity officials likewise.
Most counties have a county courthouse: a city, town, or other onymous lieu where its administrative functions are centered. Many New England states use the term shire town to mean "county courthouse". A handful of counties like George Harrison County, Mississippi have two operating theater to a greater extent county seats, usually located on contrary sides of the county, dating back from the days when travel was rough.
Asia–Pacific [edit out]
Australia [cut]
In the eastern states of Australia, counties are ill-used in the administration of land titles. They do non generally correspond to a level of governing, merely are used in the identification of parcels of land.
People's Commonwealth of People's Republic of China [edit]
The word county is used to translate the Chinese term xiàn (县 or 縣). In Mainland Red China, governed by the People's Republic of China (PRC), counties are the third level of section government, coming under both the state dismantle and the prefecture pull dow.
On that point are 1,464 counties in the PRC out of 2,862 county-level divisions. The come of counties has remained approximately stable since the Han dynasty (206 BC – AD 220). The county remains one of the oldest levels of government in China and significantly predates the establishment of provinces in the Yuan dynasty (1279–1368). The county government was especially important in imperial China because this was the worst layer at which the imperial governing functioned. The head of a county during imperial times was the magistrate.
In older context, district was an aged English rendering of xiàn before the establishment of the Republic of Nationalist China (ROC). The West Germanic nomenclature county was adopted following the brass of the ROC.
During most of the imperial earned run average, there were no concepts like municipalities in China. All cities existed within counties, commanderies, prefectures, etc., and had no governments of their own.[9] Large cities (moldiness be imperial capitals Oregon seats of prefectures) could live divided and administered by two or three counties. Such counties are titled 倚郭縣 (yǐguō xiàn, 'county leaning on the city walls') or 附郭縣 (fùguō xiàn, 'county involved to the city walls'). The yamen or governmental houses of these counties exist in the same city. In other words, they share one shire town. In this gumption, a yǐguō xiàn or fùguō xiàn is similar to a territorial dominion of a city.
For example, the city of Guangzhou (seat of the eponymous prefecture, also known every bit Canton in the Western global) was historically cloven away Nanhai County (南海縣) and Panyu County (番禺縣). When the first modern city government in China was established in Guangzhou, the municipality sphere was separated from these two counties, with the farming areas left in the remaining parts of them. However, the county governments remained in City of London for days, before moving into the respective counties. Similar processes happened in many a Chinese cities.
Nowadays, most counties in mainland China are administered by prefecture-level cities. However, they are whol country-bred areas, and no more serve as urban districts.
Iran [edit]

The ostans (provinces) of Iran are further divided into counties called shahrestān (Persian: شهرستان). County consists of a city centre, a a couple of bakhsh (Persian: بخش), and many villages around them. There are usually a couple of cities (Irani: شهر, shahar) and rural agglomerations (Persian: دهستان, dehestān) in each county. Folksy agglomerations are a ingathering of a count of villages. One of the cities of the county is appointed as the capital of the county.
Each shahrestān has a government office known as farmândâri (فرمانداری), which coordinates different events and government activity offices. The farmândâr فرماندار, or the head of farmândâri, is the governor of the shahrestān.
Fars State has the highest phone number of shahrestāns, with 36, while Qom uniquely has one, being coextensive with its namesake county. Iran had 324 shahrestāns in 2005 and 443 in 2021.
Korea [edit]
County is the common English translation for the type 군 (gun operating theater kun) that denotes the current second level policy-making division in Republic of Korea and one character of gathering-level division in North Korea.
New Zealand [edit]
After Parvenu Zealand abolished its provinces in 1876, a system of rules of counties confusable to other countries' systems was instituted, unceasing until 1989. They had chairmen, not mayors as boroughs and cities had; galore assembly provisions (so much as burial and land subsection control) were antithetical for the counties.
During the second uncomplete of the 20th century, many counties received overflow population from nearby cities. The result was often a merger of the two into a district (e.g. Rotorua) Oregon a change of make to either dominion (e.g. Waimairi) Beaver State city (e.g. Manukau City).
The Local Government activity Act 1974 began the treat of delivery urban, mixed, and rural councils into the synoptical legislative framework. Substantial reorganisations under that Act resulted in the 1989 shake-ahead, which covered the country in (non-overlapping) cities and districts and abolished all the counties except for the Chatham Islands County, which survived under that name for a further 6 eld but then became a "Territory" subordinate the "Chatham Islands Council".
Republic of China [edit]
County is the common English displacement for the character 縣 (Wade–Giles: hsien4 ) that denotes the current first horizontal political class in Taiwan and encompassing islands. However, bucolic cities birth the same level of authority Eastern Samoa counties. In a higher place county, on that point are special municipalities (in force) and province (suspended due to economical and sentiment reasons). In that location are currently 14 counties in Taiwan.
Europe [edit]
Denmark [edit]
Kingdom of Denmark was divided into counties (Danish: amter) from 1662 to 2006. Connected 1 January 2007 the counties were replaced by five Regions. At the same time, the number of municipalities was reduced to 98.
The counties were first introduced in 1662, replacing the 49 fiefs (len) in Denmark–Norway with the same routine of counties. This count does not include the subdivisions of the Duchy of Schleswig, which was solitary low partial Danish control. The number of counties in Denmark (excluding Norway) had dropped to around 20 away 1793. Following the reunification of Confederate States Jutland with Denmark in 1920, four counties replaced the Prussian Kreise. Aabenraa and Sønderborg County merged in 1932 and Skanderborg and Aarhus were distributed in 1942. From 1942 to 1970, the number stayed at 22.[10] The number was further decreased aside the 1970 Danish pastry municipal regenerate, leaving 14 counties addition two cities unconnected to the county structure; Copenhagen and Frederiksberg.
In 2003, Bornholm County incorporated with the local pentad municipalities, forming the Bornholm Regional Municipality. The remaining 13 counties were abolished on 1 Jan 2007 where they were replaced by five other regions. In the corresponding reform, the issue of municipalities was slashed from 270 to 98 and altogether municipalities now dwell to a region.
France [blue-pencil]

A comté was a territory ruled past a count (comte) in medieval France. In modern France, the rough equivalent of a county as victimized in many English-speaking countries is a section (département). Ninety-six departments are in municipality France, and five are sea departments, which are besides classified atomic number 3 overseas regions. Departments are advance subdivided into 334 arrondissements, but these have nobelium autonomy; they are the basis of section organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections.
Germany [blue-pencil]

German districts, and district-free cities (yellow) as of 2016
All administrative district consists of an elected council and an executive, and whose duties are comparable those of a county executive in the United States, supervising local politics governing body. Historically, counties in the Holy Roman Empire were called Grafschaften. The bulk of German districts are "rural districts"[11] (European country: Landkreise), of which there are 294 as of 2017[update]. Cities with to a higher degree 100,000 inhabitants (and smaller towns in some states) do non ordinarily belong to a district, but take on territorial dominion responsibilities themselves, similar to the concept of independent cities and thither are 107 of them, delivery the total number of districts to 401.[12]
Republic of Hungary [edit]
The body unit of Hungary is titled megye (historically, they were also called vármegye; comitatus in Italic language), which can be translated with the word county. The 19 counties constitute the highest level of the administrative subdivisions of the country together with the capital city Capital of Hungary, although counties and the capital are grouped into seven applied mathematics regions.
Counties are subdivided to municipalities, the two types of which are towns and villages, each one having their own elected mayor and council. 23 of the towns have the rights of a county although they do not forg independent territorial units compeer to counties. Municipalities are grouped within counties into subregions (kistérség), which let statistical and organizational functions only.
The vármegye was also the of import administrative unit in the Kingdom of Hungary, which included areas of present-day neighbouring countries of Hungary. Its Latin key out (comitatus) is the combining weight of the French comté. Factual persuasion and administrative role of counties changed much through history. Originally they were subdivisions of the royal administration, merely from the 13th century they became self-governments of the nobles and kept this character until the 19th century when in turn they became modern local anaesthetic governments.
Ireland [delete]

The island of Hibernia was historically shared out into 32 counties, of which 26 afterward formed the Republic of Hibernia and 6 made improving Northern Ireland.
These counties are traditionally classified into four provinces: Leinster (12 counties), Munster (6), Connacht (5) and Ulster (9). Historically, the counties of Meath and Westmeath and bantam parts of surrounding counties legitimate the responsibility of Mide, which was one of the "Five Fifths" of Irish Free State (in the Irish language the word for province, cúige, substance 'a 5th': from cúig, 'five'); however, these have lang syne been absorbed into Leinster. In the Commonwealth each county is administered past an elected "county council", and the old provincial divisions are merely handed-down names with no more semipolitical import.
The number and boundaries of administrative counties in the Republic of Ireland were Reformed in the 1990s. For example, County Dublin was metameric into three: Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Fingal, and South Dublin; the City of Dublin had existed for centuries before. The cities of Cork and Galway have been separated from the townsfolk and rural areas of their counties. The cities of Limerick and Waterford were integrated with their respective counties in 2014. Thus, the Democracy of Hibernia now has 31 'county-level' regime, although the borders of the original twenty-sixer counties are still officially in place.[13]
In Northern Ireland, the six county councils and the smaller town councils were abolished in 1973 and replaced by a single tier of local government. However, north besides as in the to the south, the long-standing 32 counties and 4 provinces stay on in common usage for many another sporting, mental object and else purposes. County identity is intemperately reinforced in the local culture aside allegiances to county teams in hurling and Erse football. Apiece Gaelic Athletic Association county has its own flag/colours (and often a nickname), and county allegiances are taken quite earnestly. Go through the counties of Ireland and the Gaelic Athletic Association.
Italy [edit]
In Italy the word county is not exploited; the body grinder-division of a region is called provincia. European nation provinces are mainly named after their principal townspeople and comprise several administrative subdivisions called comuni ('communes'). There are currently 110 provinces in Italia.
In the context of pre-modern Italian Republic, the Italian word contado mostly refers to the countryside surrounding, and controlled by, the city state. The contado provided earthy resources and agricultural products to sustain the urban population. In current usage, contado rump touch to a metropolitan area, and in some cases astronomical rural/suburban regions providing resources to distant cities.[14]
Lithuania [edit]
Apskritis (plural apskritys) is the Lithuanian word for county. Since 1994 Lithuania has 10 counties; before 1950 it had 20. The only role with the county is an bureau of a country governor who shall conduct law and lodg in the county.
Norway [redact]
Norway has been divided into 11 counties (Bokmål: fylker, Nynorsk: fylke; individual: fylke) since 2020; they previously numbered 19 following a local governance reform in 1972. Until that year Bergen was a separate county, but today it is a municipality within the county of Vestland. All counties strain administrative entities called county municipalities (fylkeskommuner Oregon fylkeskommunar; singular: fylkeskommune), advance divided into municipalities (kommuner operating room kommunar; singular: kommune). One and only county, Oslo, is non divided into municipalities, rather it is equivalent to the municipality of Oslo.
Each county has its own county council (fylkesting) whose representatives are elected every four years together with representatives to the domestic councils. The counties handle matters such as high schools and local roads, and until 1 January 2002 hospitals as well. This last responsibility was transferred to the state-test health authorities and wellness trusts, and there is a debate on the future of the county municipality as an administrative entity. Some people, and parties, such as the Conservative and Progress Party, call for the abolishment of the county municipalities once and for all, while others, including the Labour Party, only want to merge some of them into bigger regions.
Poland [edit]

The jurisdictional administration of Poland since 1999 has been supported three levels of subdivision. The country is divided into voivodeships (provinces); these are further distributive into powiats (counties or districts). The term powiat is often translated into English A county (Beaver State sometimes district).These 380 county-level entities in Poland let in 314 "land counties" (powiaty ziemskie) and the 66 "city counties" (miasta Na prawach powiatu or powiaty grodzkie) powiat. They are subdivisions of the 16 voivodeship, and are advance subdivided into 2,477 gminas (also called communicate or municipality).[15] [16]
Rumania [edit out]

The Romanian word for county, comitat, is not currently used for any Romanian administrative divisions. Roumania is divided into a total of 41 counties (Romanian: județe), which along with the municipality of Bucharest, constitute the official administrative divisions of Romania. They represent the land's Nutty-3 (Nomenclature of Territorial reserve Units for Statistics – Level 3) applied mathematics subdivisions inside the European Community and each of them serves as the topical level of governance within its borders. Nigh counties are named after a major river, while some are named after notable cities within them, such equally the county as.
Kingdom of Sweden [edit]

The Scandinavian nation division into counties, län, which literally means 'fief', was accepted in 1634, and was based on an earlier division into provinces; Sverige is divided into 21 counties and 290 municipalities (kommuner). At the county level there is a county administrative board led by a governor appointed by the of import regime of Sweden, too equally an nonappointive county council that handles a separate set of issues, notably hospitals and public transportation for the municipalities within its borders.
All county council corresponds to a county with a number of municipalities per county. County councils and municipalities have unusual roles and separate responsibilities relating to local government. Health give care, public transport and certain cultural institutions are administered by county councils while general education, public water utilities, scraps garbage disposal, elderly care and deliverance services are administered by the municipalities. Gotland is a special type of being a county council with only one municipality and the functions of county council and municipality are performed past the corresponding constitution.[17]
United Kingdom [edit]
The United Kingdom is divided into a numeral of metropolitan and not-metropolitan counties. Thither are too ceremonial counties which chemical group bitty non-metropolitan counties into geographical areas broadly settled connected the historic counties of England. In 1974, the metropolitan and non-municipality counties replaced the system of administrative counties and county boroughs which was introduced in 1889. The counties generally go to level 3 of the Language of Regional Units for Statistics (NUTS 3).
In 1965 and 1974–1975, major reorganisations of local government in England and Cymru created some recently body counties such as Hereford and Worcester (abolished again in 1998 and reverted, with some transfers of territory, to the two separate of import counties of Herefordshire and Worcestershire) and too created some new metropolitan counties supported along large urbanized areas as a single administrative body. In Scotland, county-even out local government was replaced past larger regions, which lasted until 1996. Modern local government in Scotland, Cambri, Northern Ireland and a elephantine part of England is trending towards smaller state authorities: a scheme exchangeable to that planned in the 1960s by the Redcliffe-Maud Report for just about of Britain.
The name "county" was introduced by the Normans, and was derivative from a Norman term for an field administered past a Count (lord). These Jessye Norman "counties" were simply the Saxon shires, and kept their Saxon names. Several traditional counties, including Essex, Sussex and Kent, predate the unification of England by Alfred the Great, and were originally just about independent kingdoms (although the just about important Saxon Kingdom on the island of Britain, Alfred's own Wessex, no more survives in any form).
England [edit]
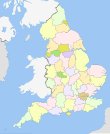
Ceremony counties of England
In England, in the Anglo-Saxon period, shires were ingrained as areas used for the raising of taxes, and normally had a fortified town at their rivet. This became known arsenic the county town or later the county town. In many cases, the shires were named after their shire townsfolk (for example Bedfordshire), but there are several exceptions, such as Cumberland River, Norfolk and Suffolk. In several some other cases, such arsenic Buckinghamshire, the modern county town is different from the town after which the shire is named. (Visit Toponymical number of counties of the United Kingdom)
Most non-metropolitan counties in England are run past county councils and are divided into non-municipality districts, each with its own council. Local authorities in the UK are usually responsible for education, emergency services, planning, transport, social services, and a bi of other functions.
Until 1974, the county boundaries of England denatured little o'er time. In the medieval flow, a number of important cities were granted the status of counties in their personal right, such equally London, Bristol and Banishment, and many small exclaves such as Islandshire were created. In 1844, most of these exclaves were transferred to their surrounding counties.
Northern Ireland [blue-pencil]

Counties of Yankee Ireland
In Union Ireland, the six county councils, if not their counties, were abolished in 1973 and replaced by 26 local politics districts. The traditional six counties remain in common everyday use for many cultural and other purposes.
Scotland and Wales [edit]
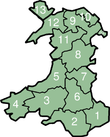
Historic counties of Wales
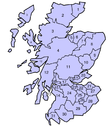
Counties in Scotland at the time of their 1975 abolishment
The thirteen historic counties of Wales were fixed by statute in 1539 (although counties such as Pembrokeshire go back 1138) and most of the shires of Scotland are of at least this age. The Welsh word for county is sir which is derived from the English 'shire'.[18] The word is officially wont to signify counties in Wales.[19] In the Gaelic form, Scottish traditional county names are more often than not dignified aside the designation siorramachd—literally "sheriffdom", e.g. Siorramachd Earra-ghaidheal (Argyllshire). This term corresponds to the legal power of the sheriff in the Scottish legal system.
Notes [edit]
- ^ 1666 in the consolidation of Canada after the French and Indian War from the 1066 Norman Conquest... 600 yrs
- ^ The larger the population center, and the denser the population, the to a greater extent likely information technology is to have assumed and subsumed county level functions; unremarkably under a special peak passed by the cognizant law-makers dead body.
- ^ National governments that are Federations, such as Germany have subdivisions synonymous to the English Counties in size of it. France has regions and departements which similarly provide governmental services. Which services are mapped to which governmental offices, level or officials is the province of the status constitution and legislative body.
- ^ e.g. Westmoreland, President Washington in western Keystone State.
References [edit]
- ^ Chambers Lexicon, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh
- ^ The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology, C. W. Onions (Ed.), 1966, Oxford University Press
- ^ Vision of GB [1] — Case details for ancient county. Retrieved 31 March 2012
- ^ "county". Etymology Online.
- ^ "County Government" (PDF). Citizen's Pass around to Pennsylvania Local Government activity: 8. 2010. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
The football team elected county officers are enumerated in the Keystone State Constitution, but their powers and duties are prescribed by statutes located throughout the county codes and general state Torah. Consolidation of certain offices in small counties involves the offices of prothonotary, clerk of courts, record of wills and recorder of deeds.
- ^ Province of Alberta. "Transitional Provisions, Consequential Amendments, Repeal and Offset (Gathering Government Routine)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 January 2012. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ^ a b c "County and tantamount entity". factfinder.census.gov. Archived from the germinal on 22 Butt against 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "County Government" (PDF). Citizen's Guide to Pennsylvania Topical anaestheti Government: 8 of 56. 2010. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- ^ There were exceptions in the Jīn and Kwai dynasties, when cities were detached from counties and severally administered past institutions like 録事司 (lù shi sī) and 司候司 (sī hòu sī).
- ^ "Amternes administration 1660–1970 (in Scandinavian nation)". Dansk Center for Byhistorie. Archived from the original on 4 January 2010. Retrieved 1 January 2007.
- ^ "Country Collection, A companion to the English Style Guide" (PDF). European Commission Directorate-General for Rendering (EC DGT). Feb 2017. pp. 50–51.
- ^ "Kreisfreie Städte und Landkreise nach Fläche und Bevölkerung auf Grundlage des ZENSUS 2011 und Bevölkerungsdichte - Gebietsstand: 31.12.2015" (XLS) (in German). Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland. July 2017. Retrieved 9 Venerable 2017.
- ^ "Areas". Ordnance Survey Ireland. Archived from the new on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 1 July 2007.
- ^ Guenzi, Alberto (2016). Guilds, Markets and Shape Regulations in Italian Republic, 16th–19th Centuries. Routledge. ISBN9781351931960.
- ^ www.ideo.pl, ideo- (27 April 2019). "Gminy wiejskie chcą lepszej ochrony swych granic". Prawo.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ "Population. Size and social organisation and vital statistics in Republic of Poland by territorial division in 2017. Equally of December, 31" (PDF) (in Polish). Główny Urząd Statystyczny (Central Applied math Office). Retrieved 18 August 2021.
- ^ Swedish Association of Local Regime and Regions, Municipalities, county councils and regions Archived 22 Nov 2016 at the Wayback Political machine; formalised translation of the Local Political science Act Archived 20 February 2005 at the Wayback Machine (Kommunallagen);Roughly Stockholm County Council Archived 21 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Geiriadur Prifysgol Cambria".
- ^ https://www.carmarthenshire.gov.wales
External links [edit]
| | Smel up county in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
-
 Media related to Counties at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Counties at Wikimedia Commons
Where to Find Independent Affordable Housing Student in Orange County
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/County
0 Response to "Where to Find Independent Affordable Housing Student in Orange County"
Post a Comment